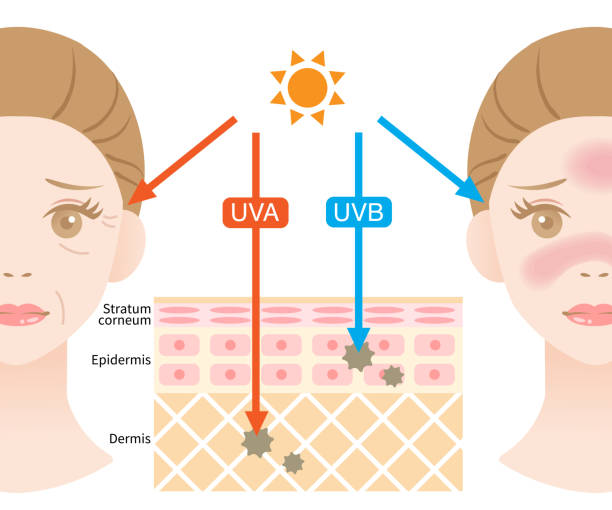
Sunlight is essential for life, but not all sun exposure is created equal. The ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun are divided into three types—UVA, UVB, and UVC. While UVC is mostly absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere and doesn’t reach us, UVA and UVB rays penetrate the atmosphere and can impact human health in both beneficial and harmful ways.
UVB (Ultraviolet B) rays from sunlight have several important health benefits, especially when exposure is moderate and controlled. Here are the key benefits:
1. Vitamin D Synthesis
-
The most well-known benefit: UVB stimulates the production of vitamin D in the skin. Vitamin D is essential for:
-
Bone health (helps absorb calcium and phosphorus)
-
Immune system support
-
Mood regulation
-
Reduced risk of autoimmune diseases, like multiple sclerosis
-
2. Improved Immune Function
-
Vitamin D from UVB exposure helps modulate the immune response, enhancing defense against infections while reducing chronic inflammation.
3. Skin Condition Treatments
-
UVB is used therapeutically to treat conditions like:
-
Psoriasis
-
Vitiligo
-
Eczema
-
-
This is often done under medical supervision via narrowband UVB phototherapy.
4. Potential Mood Benefits
-
By helping produce vitamin D and regulating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, UVB can indirectly support mental health and reduce the risk of seasonal affective disorder (SAD).
5. Circadian Rhythm Support
-
Like UVA, UVB exposure in the morning may help reinforce a healthy sleep-wake cycle, indirectly benefiting sleep and energy levels.
Caution: Too much UVB can cause sunburn, DNA damage, and increase the risk of skin cancer, so balance and protection are essential.
Best Time of Day
-
Midday (10 a.m. – 2 p.m.) is generally when the sun is highest and UVB rays are strongest.
-
This is also when your body can make the most vitamin D in the shortest amount of time.
How Much Exposure Do You Need?
-
Varies by skin tone, location, season, and clothing:
-
Fair skin: ~10–20 minutes, a few times per week
-
Darker skin: May need 30–60 minutes or more, as melanin blocks UVB
-
-
Expose arms and legs or face and arms (without sunscreen) during this short period.
Tips for Safety
-
Don’t overdo it: Get just enough sun to slightly pink the skin (if you’re fair) — not burn.
-
Avoid sunburn: Once you’ve reached your sun time, apply sunscreen or seek shade.
-
No glass windows: UVB doesn’t penetrate glass, so outdoor exposure is necessary.
-
Latitude and season matter: In winter or in far northern/southern areas, UVB may be too weak — supplements or UVB lamps may help.
For more detailed information, check out:
👉 American Academy of Dermatology – UV Radiation